Gene Therapy Pipeline
How does it work
What is Gene Therapy
Human gene therapy seeks to modify or manipulate the expression of a gene or to alter the biological properties of living cells for therapeutic use. Gene therapy is a technique that modifies a person’s genes to treat or cure disease. Gene therapies can work by several mechanisms: Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene, inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly, and introducing a new or modified gene into the body to help treat disease. Gene therapy products are being studied to treat diseases including cancer, genetic diseases (like hearing loss and deafness), and infectious diseases.

Gene Therapy products are becoming medically and commercially viable.
2023
Status Of RHI Product Line
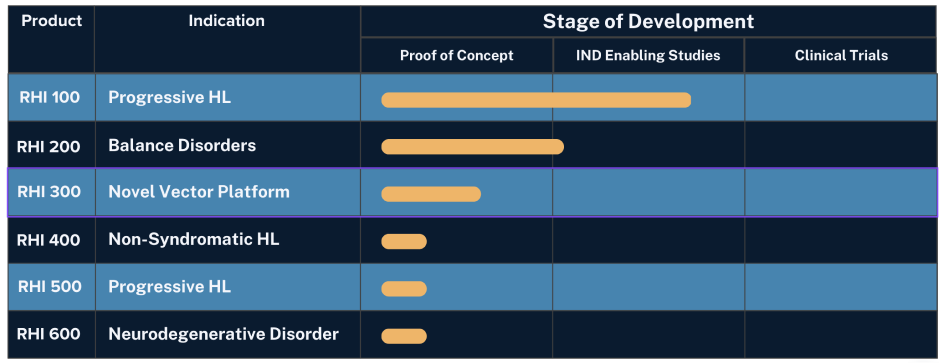
Our Products
Developing Therapeutic Solutions for Hearing Loss
RHI 100
Targets individuals born with progressive hearing loss.
RHI 200
RHI 300
RHI 400
Targets major cause of non-syndromic hearing loss. POC studies underway.
RHI 500
Targets hearing loss prevalent in the Cochlear Implant population. POC studies underway.
